ColorDx® CCTHD®
High-Precision Diagnostic Color Vision Testing
Color vision and contrast sensitivity are important functions of the visual system, which may be affected by many diseases, disorders and common drugs and substances.
Understanding if and how much visual function is affected may assist clinical decision making and augment conversations with your patients.
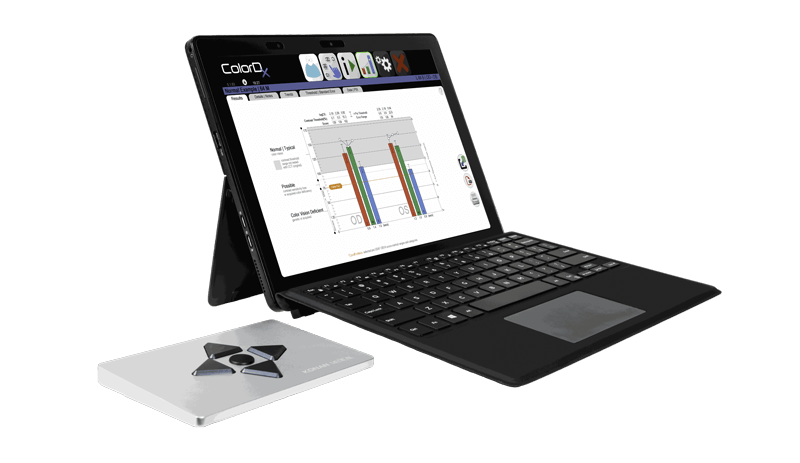
ColorDx® CCTHD®
The gold standard in diagnostic color vision testing
Developed in collaboration with the U.S. Air Force School of Aerospace Medicine OBVA (Operational Based Vision Assessment) laboratory under CRADA, CCTHD® expands on the strengths of the original USAF cone-isolation contrast test (Rabin CCT) and is built from the ground up with entirely new architecture.
Highlights include:
- Cone-isolation contrast sensitivity methodology
- Expanded low-contrast range testing
- “Landolt C” based test strategies
- Simple to use 4-button response pad
- Robust Bayesian threshold with standard error
- Konan custom-calibrated IPS matte display technology
- Rapid, intuitive, staged calibration
- High fidelity cone-contrast granularity
- Expansive illustrated reporting
- Auto trends analysis
- Contrast Sensitivity (achromatic) with auto AUC calculation
- …and much more

Clinical Applications
Other disorders of the retina or optic nerve
Pre and post cataract surgery
Vocational, avocational, and scholastic color
vision testing
Track the effect of supplements over time2
ColorDx® is not cleared for the specific diagnosis of any condition
Clinical Benefits
Detect subtle changes missed by books, plates, and other color vision tests
Compare structure & function, especially when subjective SAP does not correlate with OCT
Inform patients about the risks, consequences and hazards related to deficiencies in their cone and achromatic contrast sensitivity
Regulatory
FDA Listed | CPT Code 92283
TGA Approved
Available in Canada
Eye Care Beyond Black and White
Color Vision Changes in Macular Disease

Andrew Browne, MD PhD
Clinical Assistant Professor, Ophthalmology
Vitreoretinal Diseases and Surgery
Gavin Herbert Eye Institute, UC Irvine Health
Visual acuity measurement is the gold standard for evaluating visual function. However, contrast and color vision are largely neglected in clinical trials. In this presentation we will discuss changes in contrast and color vision associated with a variety of clinical disease states starting at the front of the eye and moving to the back.
Clinical Benefits of Diagnostic Color Vision Testing
1 in 5 may have a color vision deficiency. Contemporary eye care includes qualitative and quantitative assessment of this important measure of visual function.
Acquired color deficiencies are commonly S-cone (blue-yellow) type, but may also affect L- and M-cones.
Acquired deficiencies are typically gender neutral and become more common with age, yet may affect up to 15%* of the general population.
This important but often overlooked clinical sign may be caused by retinal, macular, optic nerve, trauma or neurological disorders, in addition to cataracts and high-risk meds, as well as hundreds of common drugs and substances**.
*Rayman, R., et al. Rayman’s Clinical Aviation Medicine. Castle Connelly. 2013. **Fraunfelder, Fraunfelder, Chambers. Clinical Ocular Toxicology. Sanders Elsevier, 2008: 320. Clinical Ocular Toxicology, Substances and Pharmaceutical Agents that can Cause Color Vision Defects
High-precision color diagnostics require high-precision calibration for highest sensitivity.
Custom-Precision Calibration
ColorDx® CCT HD® devices are individually, precision calibrated at manufacturing prior to customer shipment.
Konan’s proprietary deep, synchronous calibration provides a high-precision baseline from which periodic verifications / calibrations are based to account for typical monitor color changes over time. CCT HD® includes a USB colorimeter for routine calibrations, typically taking only about a minute.

- Clinical and Scientific Publications
- Fundamentals
- Key Features
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Product Specifications
Scientific and Clinical Publications
Summary of Independent Evaluation of Konan Medical CCT HD
“The CCT HD, with very precise color calibration, can achieve the very low cone contrast values needed to accurately quantify cone contrast thresholds even for CVN (Color Vision Normal) individuals. The capability to test CVN individuals is essential in order to research the relationship between color vision and operationally relevant performance.
Additionally, the CCT HD, with precise calibration and excellent test-retest reliability can also enable early detection of disease, improved ability to quantify the effect of hypoxia and other environmental stressors on vision, and improved ability to investigate the potential effects of chemicals/pharmaceuticals.
The precise calibration also enables binocular testing, which is not possible with the RCCT (Rabin CCT) due to the ceiling effect. The RCCT was a substantial improvement over PIP tests (e.g., Ishihara) when it was introduced, and the CCT HD is a substantial improvement over other commercially available CCTs. ”
Evaluation of Konan Medical CCT HD
James Gaska, Marc Winterbottom, and Steve Hadley 711 HPW/RHBC OBVA Laboratory Eleanor O’Keefe, Elizabeth Shoda, and Alex Van Atta KBR, Inc.; 2021 Feb.
Air Force Research Laboratory 711th Human Performance Wing Airman Systems Directorate Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, OH 45433 Air Force Materiel Command United States Air Force
Evaluation of Konan Medical CCT HD: Feb 2021 Final Report
James Gaska, Marc Winterbottom, and Steve Hadley 711 HPW/RHBC OBVA Laboratory Eleanor O’Keefe, Elizabeth Shoda, and Alex Van Atta KBR, Inc. ; 2021 Feb.
Operational Based Vision Assessment Cone Contrast Test: Description and Operation
Gaska J, Winterbottom M, van Atta A. Operational Based Vision Assessment Cone Contrast Test: Description and Operation. USAF School of Aerospace Medicine, Aeromedical Research Department Wright-Patterson AFB; 2016 Jun 1.
The Diabetes Visual Function Supplement Study (DiVFuSS)
Chous AP, Richer SP, Gerson JD, Kowluru RA. The diabetes visual function supplement study (DiVFuSS). British Journal of Ophthalmology. 2015 Jun 17:bjophthalmol-2014.
Evaluation of Acquired Color Vision Deficiency in Glaucoma Using the Rabin Cone Contrast Test
Niwa Y, Muraki S, Naito F, Minamikawa T, Ohji M. Evaluation of Acquired Color Vision Deficiency in Glaucoma Using the Rabin Cone Contrast TestRabin Test for Glaucoma Color Vision Deficiency. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science. 2014 Oct 1;55(10):6686-90.
Rabin Color Cone Contrast Testing and Retinal Structure in Multiple Sclerosis
Samuel A, Yiu H, Songster C, Bolivar D, Gelfand J, Green A. Rabin Color Cone Contrast Testing and Retinal Structure in Multiple Sclerosis (P3. 227). Neurology. 2015 Apr 6;84(14 Supplement):P3-227.
Evaluation of visual function impairments in patients with dry age-related macular degeneration
Lad EM, Chandramohan A, Ventura A, Cousins SW. Evaluation of visual function impairments in patients with dry age-related macular degeneration. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2014 Apr 30;55(13):5213-.
Rapid Quantification of Color Vision: The Cone Contrast Test
Rabin J, Gooch J, Ivan D. Rapid quantification of color vision: the cone contrast test. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science. 2011 Feb 1;52(2):816-20.
Evaluation of clinical validity of the Rabin conecontrast test in normal phakic or pseudophakiceyes and severely dichromatic eyes
Fujikawa M, Muraki S, Niwa Y, Ohji M. Evaluation of clinical validity of the Rabin cone contrast test in normal phakic or pseudophakic eyes and severely dichromatic eyes. Acta Ophthalmologica. 2017 May 31.
A Performance Comparison of Color Vision Tests for Military Screening
Walsh DV, Robinson J, Jurek GM, Capó-Aponte JE, Riggs DW, Temme LA. A Performance Comparison of Color Vision Tests for Military Screening. Aerospace medicine and human performance. 2016 Apr 1;87(4):382-7.
A Monte Carlo simulation of four contrast threshold estimation techniques: clinical vision test selection for operationally-based vision assessment
Winterbottom, M., J. P. Gaska, S. T. Wright, and J. M. Gooch. “Monte Carlo simulation of four contrast threshold estimation techniques: clinical vision test selection for Operationally-Based Vision Assessment.” Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine 83, no. 3 (2012).
Fundamentals
Fundamentals of Cone-isolation Contrast Sensitivity
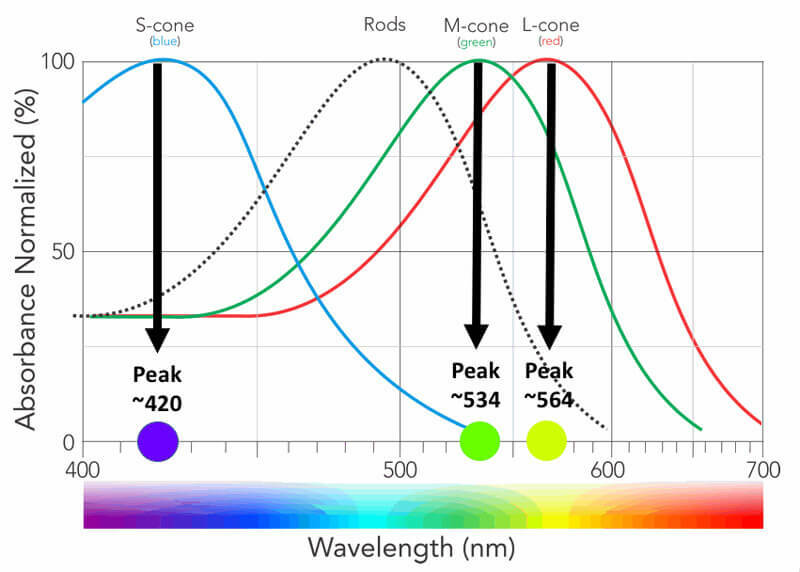
CCT HD is based upon the principle of stimulating individual cone type populations, L-cone (long wavelength), M-cone (medium), and S-cone (short). Each cone population has offset peak sensitivities and broad ranges of sensitivities. Although L-cones are often referred to as “red”, M-cones as “green”, and S-cones as “blue”, peak sensitivity wavelengths of the cone populations are colors not fitting these descriptions.
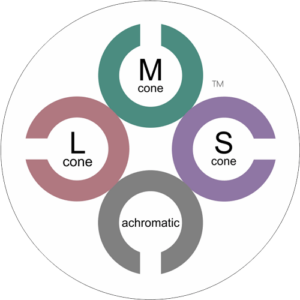
CCT HD tunes the calibrated stimulus color composition to simultaneously maximize the response of a targeted cone population, minimize, as negligible, the response of non-targeted cones, and neutralize achromatic (brightness) cues.
L-cones have the best sensitivity of the 3 cones for “red” wavelengths, but with a peak sensitivity that is not “red”. M-cones have strongest sensitivity for “green” wavelengths and S-cones have the strongest sensitivity for blue and violet wavelengths. There is little wonder why many emergency vehicles are colored in the range of the peak sensitivity of the largest cone populations where there is the highest sensitivity from our central vision.

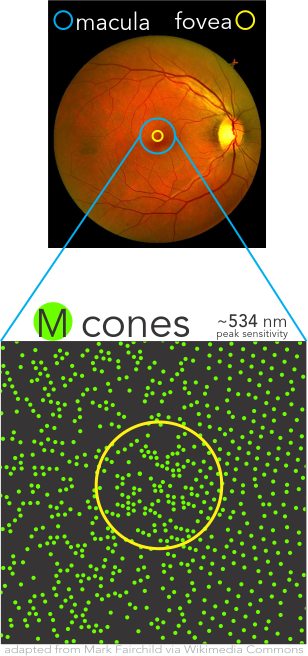
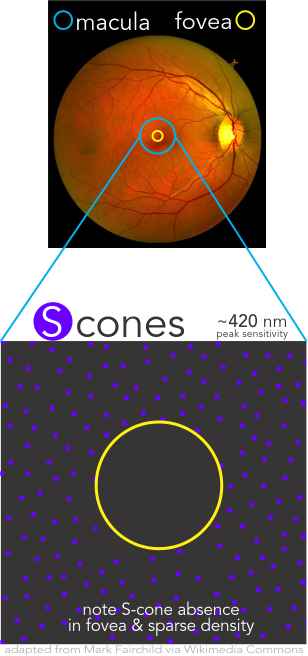
Cone Populations Importance
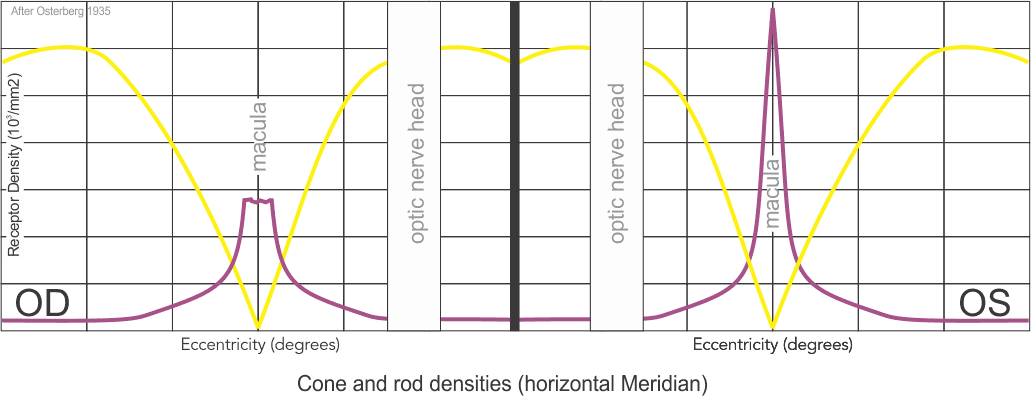
Densities of the individual cone populations are asymmetric with L-cones making up over one-half, M-cones over one-third, and S-cones less than 10% and uniquely being completely absent from the Fovea Centralis.
Cortical interpretation of the mix of differential responses of the cones drive the percept of color using multiple mechanisms, such as (L-M), S – (L+M), and brightness with L+M. Precision assessment of these aspects are simply not available with most historical methods of color vision testing.
Cone Density
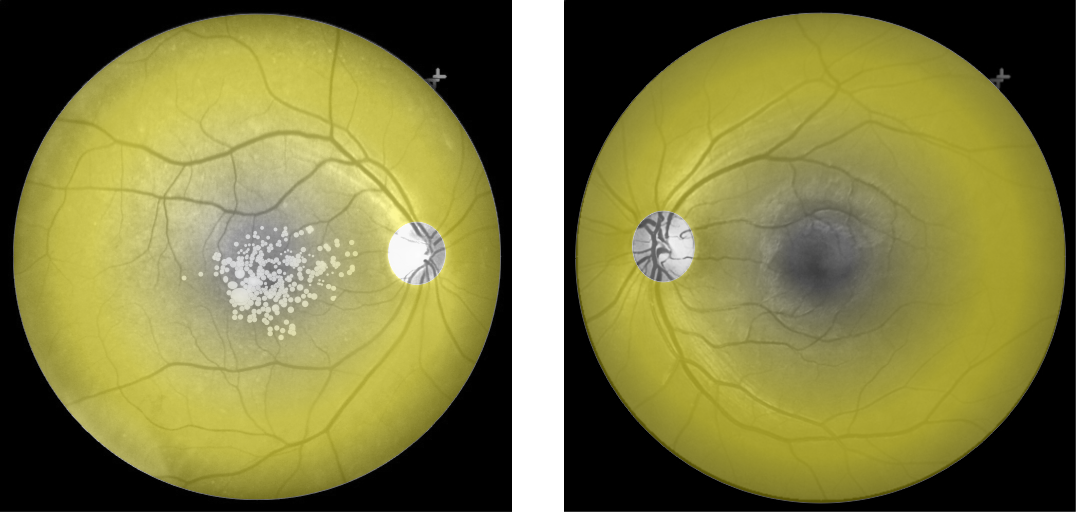
Cones density (illustrated here as a “violet” pseudo-color overlay) is highest at the macula rapidly becoming sparse to the peripheral retina with rods (density illustrated here as “yellow”) having a complement density distribution. With the high concentration of cones in human central vision, it is no wonder that Konan’s core interest in the medical/clinical ramifications of cone function, as a functional vision test assessed with cone-isolation contrast sensitivity, is in it’s importance as a tool for physicians to better understand onset and changes that may manifest from acquired conditions, such as those affecting retina and macula.
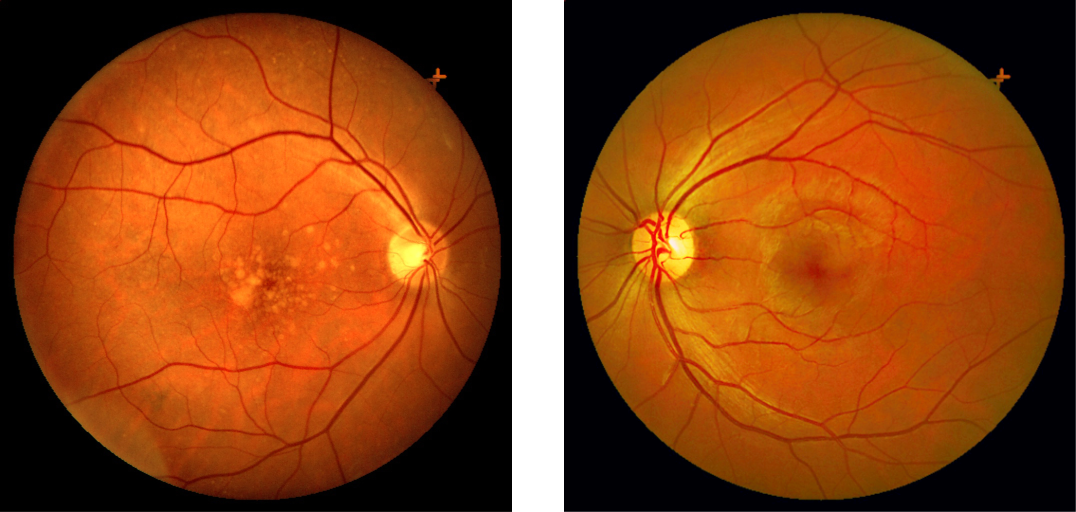
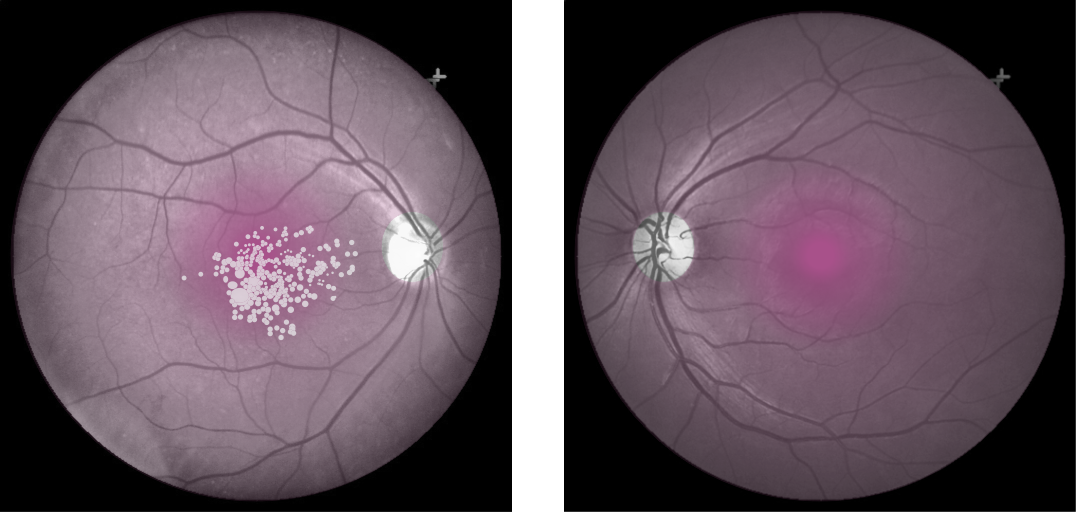
Move center slider handle to reveal the cone density illustration (violet overlay). The pseudo-colored image on left also illustrates and highlights the damage from macular degeneration and its effect on loss of critical areas of cone density and function.



CCT HD Test Structure
The CCT HD test is structured with a series of language / literacy neutral Landolt C optotypes presented sequentially at a fixed visual angle against a defined grey background over a range contrast values from the background, exactly a contrast sensitivity test but not
achromatic as with conventional contrast sensitivity testing.
The subject simply indicates, on a for-purpose large 4 button arrow response pad, the observed direction of the opening of the “C”, forced-choice, with a simultaneous auditory response cue. Cue context is operator defined.
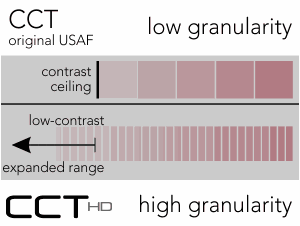
High Fidelity Testing: Importance of Granularity
CCT HD critically requires a high-precision color display with verified technical characteristics. After a dual synchronous calibration, CCT HD creates precision, repeatable very-low contrast values to extend cone contrast testing to approximate the limit of human perception. Along with precision color rendition, negligible inclusion of color contaminations from the not-targeted cone populations, provides characteristics needed to create “High Fidelity” cone-isolation contrast sensitivity utilizing highly granular stimulus steps.
(low contrast “ceiling” removed)
had low contrast “ceiling”
High Fidelity Testing: Importance of Low Contrast Range
With the availability of very-low contrast targets, CCT HD eliminates the low-contrast “ceiling” that binned most “normal” performing individuals into a single category. The US Air Force determined that this single bin actually was comprised of a normal distribution of results that may be important for assessing changes over time even in the normal populations. A system that reliably can display very-low contrast values (~0.25%) is essential to adding this extended low contrast range.
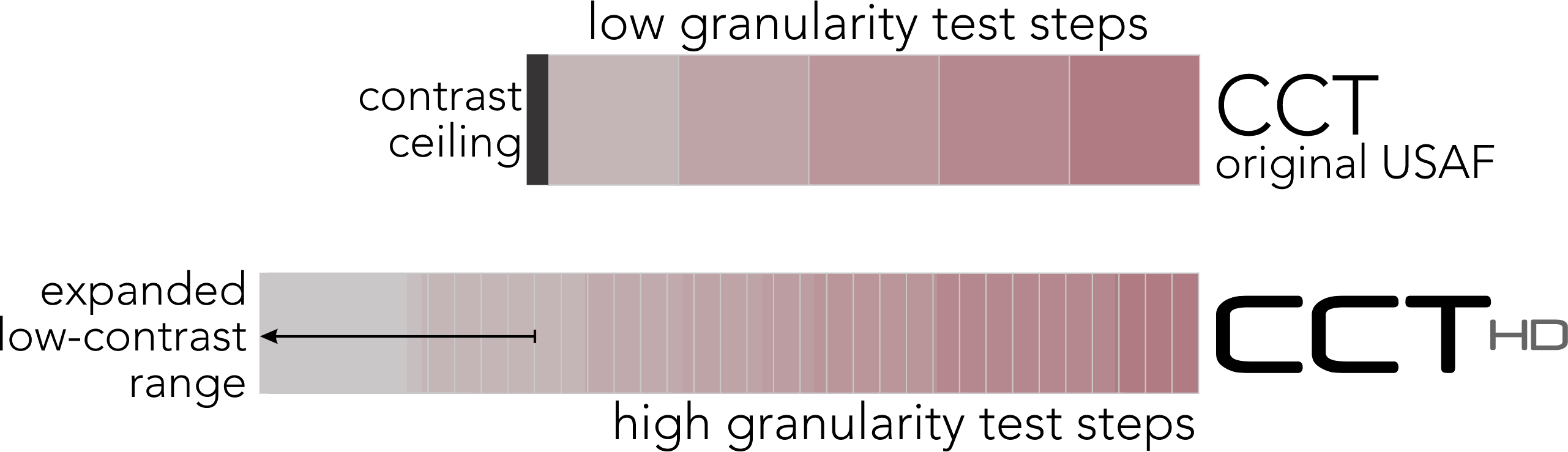
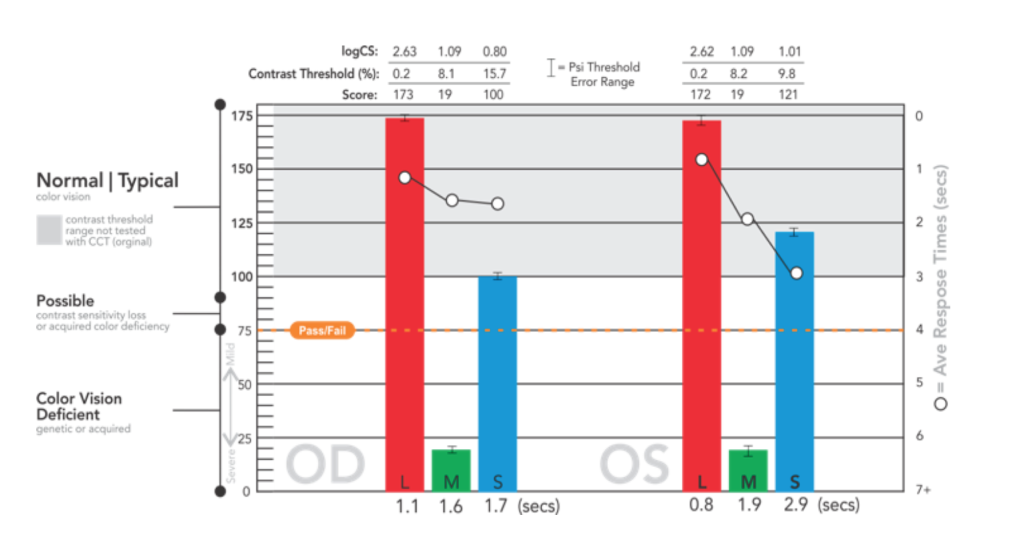
Why Bayesian Thresholding?
The Bayesian threshold method, “Psi Marginal Adaptive” technique, dynamically calculates, from prior responses, each successive test target contrast value until the threshold for each cone population is derived. This dynamic calculation streamlines “zeroing in” on the contrast thresholds, which are reported as Log CS, % contrast, and a score for convenience of comparison for users of the original USAF CCT test.
Particularly useful for clinical trials, statistical Standard Error calculations and trends analysis with prior tests, are automatically reported. A “high-precision, marginal threshold logic” is also available (developed with USAF School of Aerospace Medicine) for assessments of knife edge cut-off criteria typically used in military qualification settings.

Cone-Isolation History
Based upon landmark research of Jeff Rabin in the 1990’s with original CCT product 2011 including peer-reviewed research from Jeff Rabin, John Gooch, and Douglas Ivan in 2011 (right) with USAF.
The US Air Force, School of Aerospace Medicine OBVA (Operational Based Vision Assessment) Team initiated a research project with global allied partners (below) and engaged Konan Medical USA under CRADA to collaborate in the development of a new cone-isolation test to enhance precision, usability and low-contrast range of functional vision testing. ColorDx CCT HD is the result of this effort commercialized late in 2017.
Key Features

Easy Testing - 4 Button Response Pad
Konan’s 4-button USB response pad provides a robust,ambidextrous response solution.
Read More
- Facilitates maintaining fixation near the test area
- Reduces uncontrolled contrast adaptation and response time variability due to visual searching for the response character
- No inadvertent testing of keyboard / mouse skills, or hunting for one of 10 letters when the focus should be on taking the test
High Granularity
CCT HD provides highly granular cone-isolation contrast steps for discrete, scalar scoring.
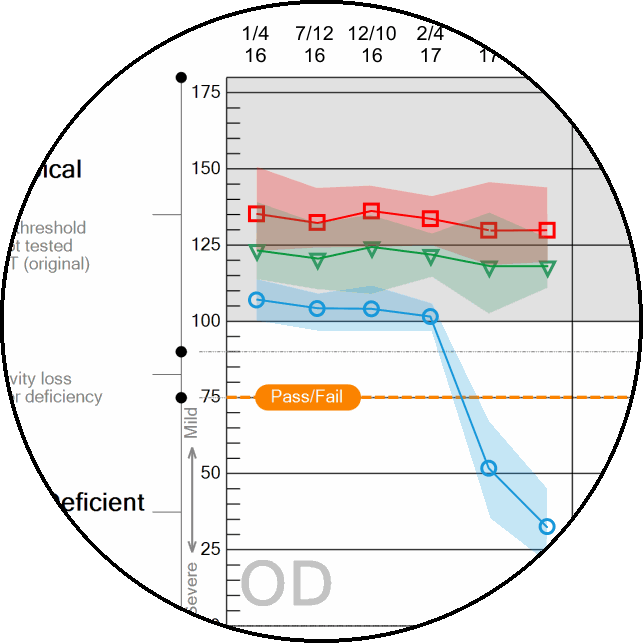
Patient color vision trends analysis
Automatically compare exam results with prior data collected on the same patient.
Read More

CE mark and FDA listed
The first and only FDA listed and CE marked cone-isolation contrast sensitivity test for color vision diagnostics from Konan Medical, an ISO-13485 company.

Robust Psi-marginal Adaptive Threshold and Error Estimation
Powerful Bayesian psychometric function for both threshold and error estimation.
Read More
- Published technique that has wide academic use
- Estimates contrast threshold and slope virtually free of bias
- Calculation of ”guess rate” from the posterior distribution
- Addresses nuisance parameters in an adaptive manner
- Background calculation of next ‘look-ahead” of calculated trials based on distribution of prior answers
- Shown to give higher precision in the threshold estimate when the threshold is designated to be the only parameter of primary interest and the slope and the lapse rate are treated as nuisance parameters
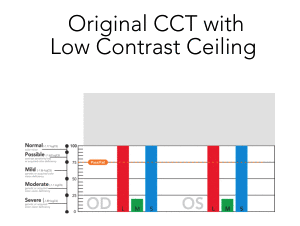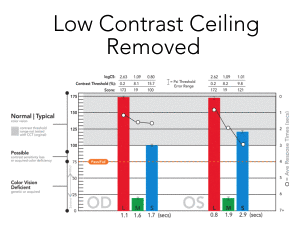
The Low Contrast Ceiling is Lifted
The original CCT was technically limited to testing down to ~ 1.0 % contrast, but this is far above the human performance threshold
Read More
- Subjects were ”binned” into 5 basic threshold levels, the lowest of which contained the majority of responses
- There is significantly more performance data uncovered by testing to < 0.3 % contrast with highly granular contrast steps down to ~ 0.25%.
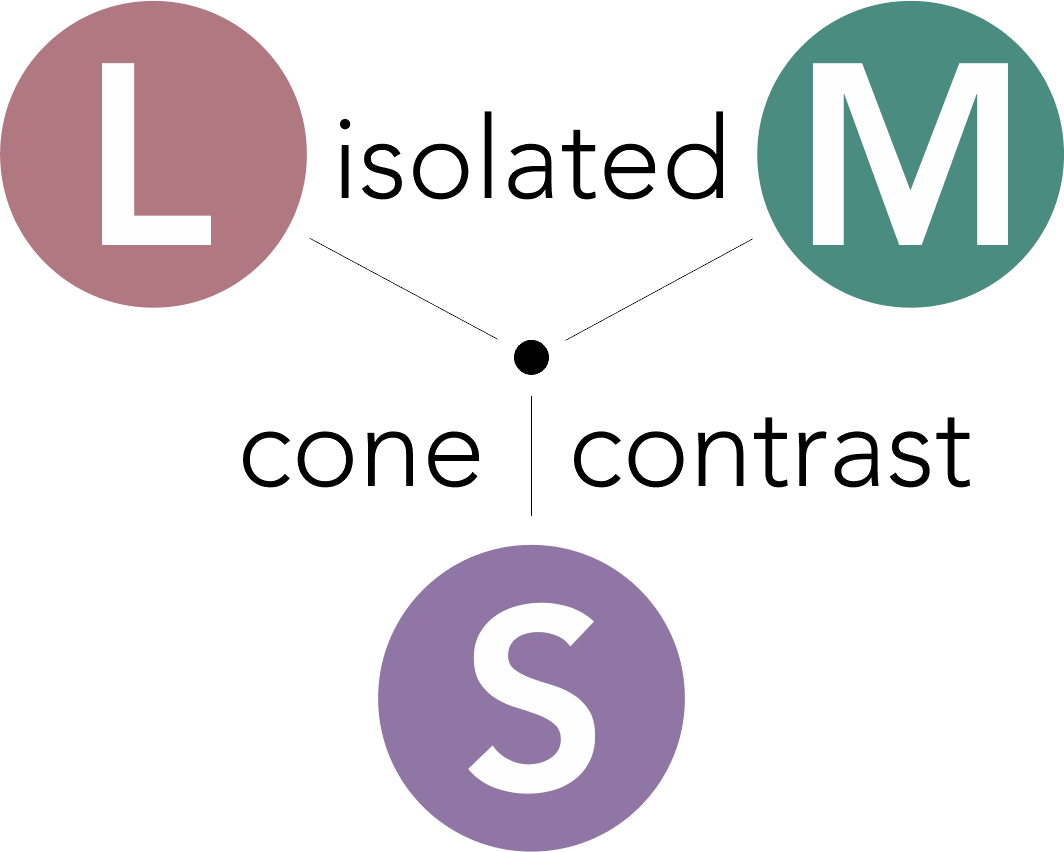
Photopic Cone Isolation
Powerful Bayesian psychometric function for both threshold and error estimation.
Read More
- Common ophthalmic tests specifying photopic conditions are variously conducted generally in the range of ~ 85 cd/m²
- CCT HD provides background luminance in the mid photopic range

Co-developed with USAF

OBVA allied partners testing cone-isolation contrast sensitivity
5+ years in development by US Air Force OBVA including global allied contributors to evaluation / clinical validation from:
Read More
- Singapore, Australia, Canada, Israel, NAMI, USAARL, University of Melbourne, University of Waterloo, York University
- Effect of hypoxia on color vision – Japan

Adaptive fast testing or Full Threshold
“Adaptive” method initiates with a stimulus sequence about one-half the number stimuli of “Full Threshold”
~1 to 2 minutes total for typical patients.
Read More

Response Time as Secondary Performance Measure
Response times can be an interesting secondary metric of subject performance
Read More

Smart, Deep Synchronous Calibration
A novel, synchronous calibration method designed specifically for CCT HD is used to custom-calibrate an IPS display to characterize the display card and display as a system.
Read More
- Reliable cone contrasts tested at less than 0.2% are required to eliminate the contrast ceiling of the original CCT and challenge the true thresholds of human vision
- Periodic in-office calibration are alerted to the user once per month and the last calibration or verification date is printed on the exam report. Importantly, CCT HD does not fully stop use of the system until recalibration is completed (triggered by the lapse of a single calendar day). The calibration process only takes minutes.

Secure 256-bit encrypted patient data
Today’s medical records, at the minimum, require secure encryption.
Read More
- CCT HD uses 256 bit encryption with admin and user-specific user names and passwords.
- CCT HD also features permission-based remote training and service as well as one-button software updates.
Solid – Secure – Robust from Konan Medical

Language and literacy neutral, no character bias, Landolt C
Read More
Easy to administer. Easy to take.
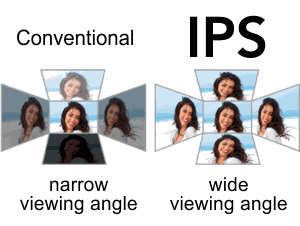
Low Sensitivity to Viewing Angle
Clear Auditory Feedback
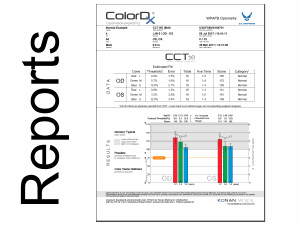
Robust, beautiful reporting
Read More
Monocular and Binocular Test Strategies & Scoring
Read More
Illustrated Help

Fully automated incremental backup
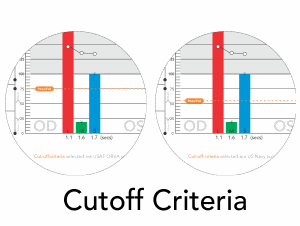
Service-Defined Pass / Fail Criteria
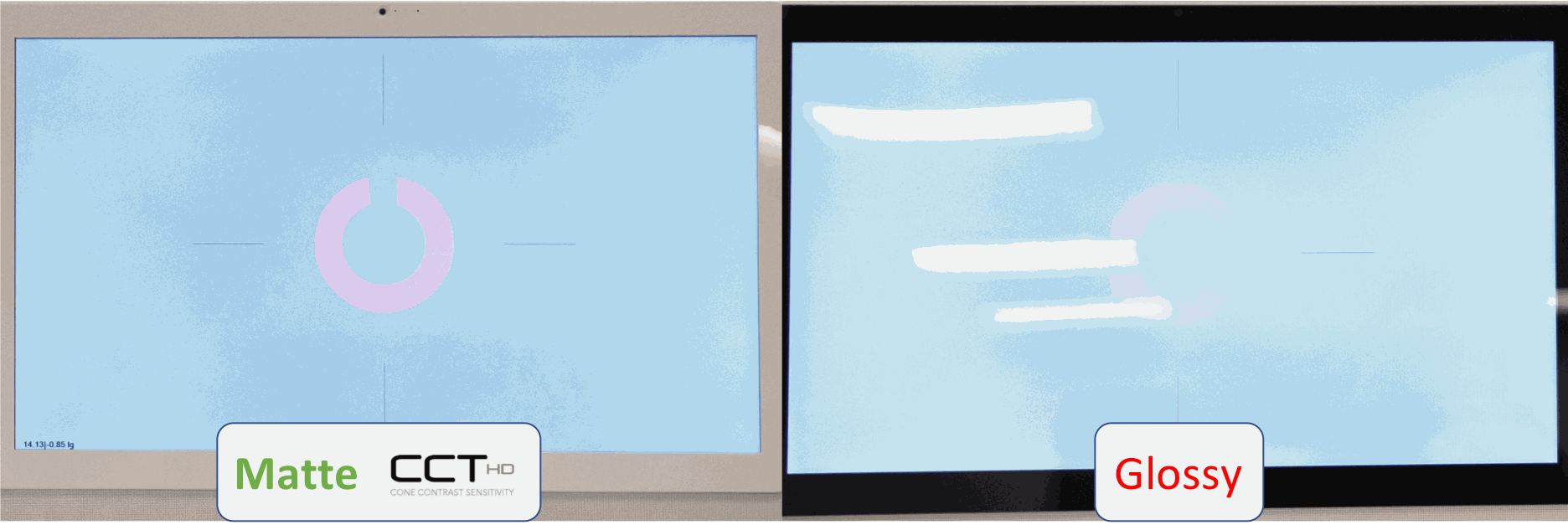
Matte Testing Monitor to Enhance Results Sensitivity
Is Color Vision Testing Reimbursable under CPT 92283 (USA customers)?
An example of detailed description of procedures, indications, and coding, documentation, and indication guidelines may be found at Decision-Maker Plus.
Importantly, it should be noted that pseudoisochomatic tests (or “PIP” tests), whether printed or digitally presented, are specifically excluded from the definition of an “extended color vision” with 92283 as “color vision testing with pseudoisochromatic plates (such as HRR, Ishihara, and others) is not reported separately but included in the appropriate general or ophthalmological service”.
Can someone who is color normal become color vision deficient?
Fraunfelder, Fraunfelder, Chambers. Clinical Ocular Toxicology. Sanders Elsevier, 2008: 320Yes. With increasing age, acquired color deficiencies become more common and can be an important sign accompanying many diseases, toxicity or side affects of many drugs and substances prescribed or used day-to-day. This important sign is frequently not tested even though a color test is administrated as common printed color vision test do not test blue type (S-cone) deficiencies (Ishihara color tests are an example of tests that do not have blue / S-cone testing features)
Different from genetic types that are quite stable through life, acquired deficiencies vary over time, are conditioned on the cause, and can progress to to severe monochromatic colorblindness. A person can have both genetic and acquired deficiencies.
There are broad categories of condtions that may lead to acquired color deficiencies:
- Trauma
- Medications
- Diseases
- Toxic Chemicals
- Age
Color Vision Deficiency Quick Facts
8% of males, more common
0.5% of females, less common
Most color perception problems are color vision “deficiencies” rather than color “blindness”
Protan type deficiencies are reduced sensitivity to red from “L-cones”. Genetically, reduced L-cone function may be due to the peak sensitivity of L-cones being closer than normal to the peak sensitivity of M-cones, and is referred to as “Protanomoly”. An absence of L-cones is the severe form, “Protan”.
Deutan type deficiencies are reduced sensitivity to green from “M-cones”. Genetically, reduced M-cone function may be due to the peak sensitivity of M-cones being closer than normal to the peak sensitivity of L-cones, and is referred to as “Deutanomoly”. An absence of L-cones is the severe form, “Deutan”.
Tritan type deficiencies are reduced sensitivity to blue from “S-cones”
Both Protan and Deutan deficiencies confuse red and green colors as being similar
Protan and Deutan deficiencies are typically genetically inherited but may also be acquired
Tritan type deficiencies are typically acquired and may be more common than genetic types
Most color deficient people see colors, but have some colors that appear the same
Most common printed color vision tests are pseudo-isochromatic or “PIP” plates and may not test for S-cone type acquired color vision deficiencies
Female color deficiencies
Acquired color deficiencies are likely to be the most common type of deficiency with women occuring generally equally in both genders and more prevelent with age.
What happened to the ColorDx Pseudo-Isochromatic ("PIP") Tests?
Pseudo-isochromatic color vision testing has historically played an important role in assessment of color vision testing for about 150 years, primarily used for for screening to identify the presence of genetic “colorblindness”. Ishihara plates, first hand watercolor painted in the early 1900’s, still are used clinically today.
The United States Air Force approached Konan Medical in 2014 to collaborate on the development of the next generation color vision diagnostic product using a contemporary “cone-isolation, contrast sensitivity” strategy. This state-of-the-art system includes expanded low contrast testing ranges, significantly higher granularity, and a robust Bayesian threshold method. The result of this research and development is ColorDx® CCT-HD*. As CCT-HD was introduced into the market, Konan also terminated its distribution of the pseudo-isochromatic products near the end of 2017, focusing exclusively on CCT-HD, which has been called the world’s finest high-fidelity test of color vision function.
Konan’s pseudo-isochromatic product customers may contact sales@konanmedical.com to receive a limited-time trade-up offer from the discontinued ColorDx® pseudo-isochromatic products.
*CCT-HD developed in collaboration with the US Air Force, School of Aerospace Medicine, Operational Based Vision Assessment Team under CRADA (Creative Research and Development Agreement).
Product Specifications
| Fundamental Method | Cone-isolation Contrast Sensitivity |
| Co-development with US Air Force | Creative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) with USAF School of Aerospace Medicine, OBVA Team |
| Laptop Computer | Dell Latitude 7320 13.3″ FHD (1920×1080) AG, Non-Touch, WVA, 250 nits, HD RGB Camera+ Mic, WLAN. Windows 10 Pro English, French, Spanish | i5-1145G7 vPro, Intel Iris XE Graphics 8GB Memory. 11th Generation Intel Core i5-1145G7 (4 Core, 8M cache, base 2.6GHz, up to 4.4GHz, vPro). M.2 256GB PCIe NVMe Class 40 Solid State Drive. |
| 4-button response pad | Konan exclusive USB answer interface eliminates letter recognition problems and hunt and peck on a keyboard or mouse |
| USB Colorimeter | OEM i1Pro with built-in fast system color verification and automated calibration |
| Reporting | On-screen PDF to network printer PDF to network EMR location |
| Testing Options | All cones, individual L, M, S cones or any combination; Monocular or binocular; Adaptive or Full Threshold; user selected test distances with dynamic optotype sizing; Tone feedback options |
| Patient Instructions and interactive demo widget | Available in multiple languages, illustrated patient instruction page includes an interactive demo to assure instructions are understood and demonstrated proficiency prior to testing including auditory feedback as “correct” tone or “miss” tone |
| Trends Analysis | Detailed trending over time by eye, by isolated cone |
| Psi Threshold | Robust, academic-based Bayesian threshold method with on-screen reporting of Standard Error estimations by response |
| Adaptive Testing | RUser-selected adaptive test seamlessly reduces test time for subjects with low standard error score |
| Achromatic Contrast Sensitivity | Contrast sensitivity reported at 4 contrast levels, and AUC indicative of overall functional vision |
| Monocular and binocular | User selected administration of tests OD and OS or OU |
| Response tones | Clear, language-independent response feedback, as high (correct) – low (incorrect) tones, or operator selected high tone only, and no auditory feedback |
| Response-time reporting | Expressly with the 4-button response pad, patient difficulty in answering is assessed as a separate measure |
| Regulatory | FDA Listed | TGA | Available in Canada |



